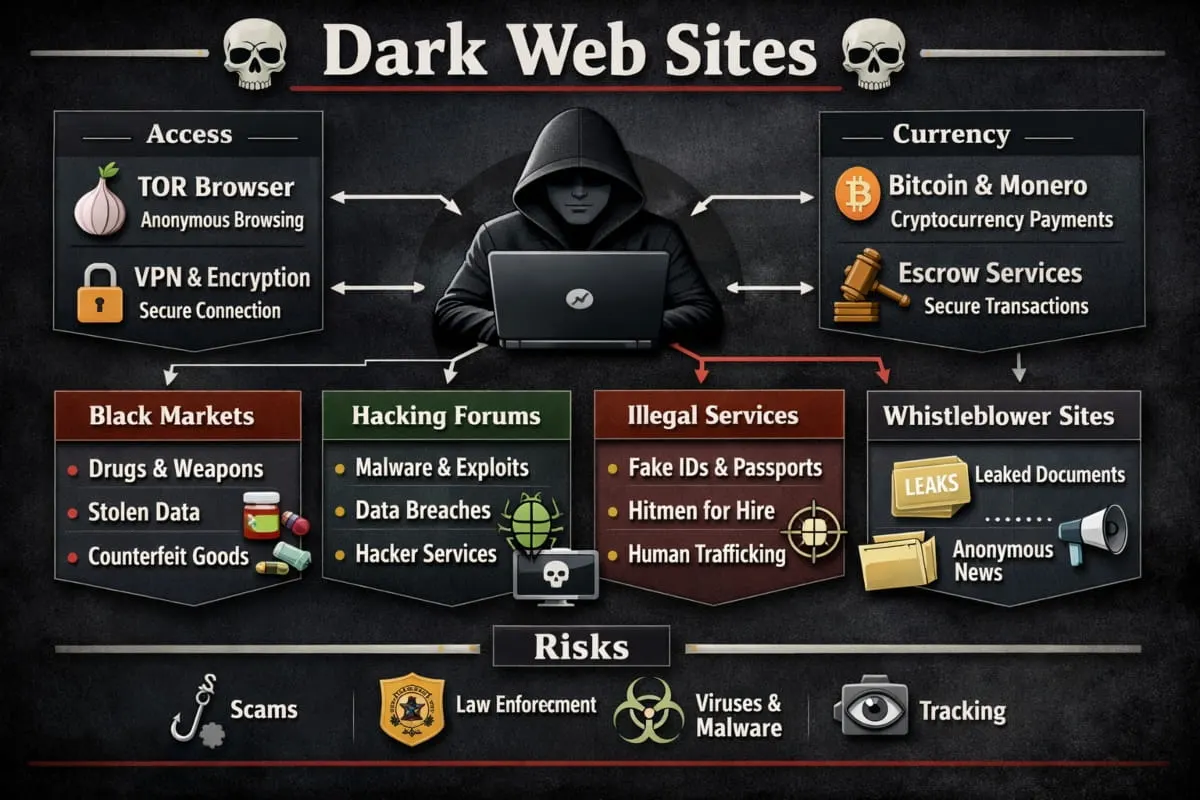
Dark web sites are websites hosted on encrypted networks like Tor that require specialized browsers to access. While some support privacy, journalism, research, and secure communication, others are associated with cyber threats and fraud. Today, cybersecurity teams, journalists, and researchers actively study the dark web to detect threats early and protect sensitive information. Understanding how this hidden layer of the internet works helps users separate myth from reality and navigate it with greater awareness and responsibility.
What Are Dark Web Sites?
Dark web sites are hosted on encrypted networks (most commonly the Tor network) and use .onion addresses, which aren’t indexed by standard search engines. You access them with special tools, and they’re used for privacy, journalism, research, and sometimes illegal activity.
Dark web sites are not the same thing as the deep web. The surface web is what Google and other engines can crawl. The deep web includes normal private content (emails, bank portals, logged-in pages). The dark web is a smaller slice that requires special access, most often through Tor, which uses onion domains.
How Dark Web Sites Work
Most dark web sites rely on the Tor network for privacy. Tor routes your connection through multiple volunteer-run servers, making it harder to trace the origin of your traffic. This system is often called onion routing because it wraps data in layers of encryption, like layers of an onion.
Here’s the simple picture:
- Tor Browser connects you to the Tor network.
- You visit onion sites using a unique .onion address.
- The connection is relayed across multiple nodes, helping protect user identity and location.
This doesn’t mean invisible, and it doesn’t automatically make everything safe. It means the network is designed to reduce traceability by adding encrypted hops between you and the destination.
Are Dark Web Sites Illegal?
No, visiting dark web sites is not automatically illegal in most places. What becomes illegal is the activity you choose to do there. Accessing the dark web (for example, using the Tor Browser to access onion sites) is generally legal, while buying, selling, or using unlawful services is not.
So the key difference is:
- Access can be legal.
- Illegal behavior is still illegal, no matter where it happens.
Types of Dark Web Sites (High-Level Overview)
The dark web includes many different categories. A single dark web site might be built for legitimate privacy needs or for harmful purposes. High-level categories include:
- News platforms: Privacy-focused versions of journalism outlets or independent publishers.
- Forums: Communities discussing privacy, technology, or niche topics.
- Whistleblower platforms: Secure submission portals designed for sensitive disclosures.
- Research databases: Archives, academic resources, or document repositories.
- Cybercrime marketplaces: Mentioned neutrally here, some dark web sites facilitate illegal trade, scams, or the sale of stolen data (avoid and report when appropriate).
This mix is why informational content should stay balanced: the dark web has real privacy use-cases, but it also attracts fraud and crime.
How Many Dark Websites Are There?
There’s no single, fixed number of dark web sites, because onion services appear and disappear frequently. Many onion sites are temporary, move addresses, or go offline, and some are intentionally hidden or restricted.
A practical way to think about it:
- The dark web is dynamic, not a stable catalog.
- Counts change constantly due to shutdowns, migrations, and new site creation.
- Even ” lists” can quickly become outdated.
Are Dark Web Sites Safe?
Not always. Even if you’re only browsing for educational reasons, dark web sites can carry real security risks. The most common threats include:
- Malware: Some sites attempt drive-by downloads or the delivery of malicious files.
- Phishing: Fake onion sites mimic real services to steal logins or information.
- Data leaks: Some spaces share breached databases and exposed personal data.
- Scams and traps: Fraud is common, including fake legit services.
If your goal is learning, treat it like cybersecurity territory: assume higher risk, keep expectations realistic, and focus on awareness—not exploration for its own sake.
Top 7 Dark Web Sites List
This list of dark websites highlights well-known, legitimate onion services that are commonly referenced for privacy, journalism, and secure communication. Rather than focusing on risky or illegal spaces, this curated overview emphasizes popular dark web sites recognized for transparency, security, and responsible use.
If you’re researching the ecosystem, these examples represent some of the most popular dark web sites operating today and demonstrate how onion services can support anonymity, censorship resistance, and information access.

Dark web sites are websites reachable via privacy networks such as Tor, using .onion addresses that traditional search engines and normal browsers don’t index. Many support legitimate privacy needs (journalism, whistleblowing, research), while others enable scams and crime. Treat every onion site as untrusted and verify addresses using official sources.
In practice, people usually mean Tor dark web sites when they say “dark web”, because Tor is the most widely used darknet for web-style onion sites.
1. DuckDuckGo (Onion Search Engine)
DuckDuckGo operates an onion version of its privacy-focused search engine, making it one of the most active dark web sites for navigation. It does not track users or store personal data, which aligns with the Tor network’s goal of anonymity.
For many users, it serves as a trusted starting point for exploring dark web onion sites, helping surface privacy-respecting resources without profiling user behavior.
A privacy-focused search engine that also operates an official onion service, useful for searching the open web without tying the query directly to a typical browsing profile. It’s a practical “starting point” because it is familiar, minimal, and privacy-focused rather than focused on content discovery for illicit markets.
Verified onion Presence: duckduckgogg42xjoc72x3sjasowoarfbgcmvfimaftt6twagswzczad.onion (listed on the organisation’s help pages).
Best for: Private search and research.
2. The Hidden Wiki (Directory Hub)
Often referenced in a dark web sites list, The Hidden Wiki is a community-edited directory that organizes links to various onion services. Think of it as a catalog rather than a recommendation engine.
Because directories can change quickly, users should approach links with caution and verify the legitimacy of any destination before trusting it.
The Hidden Wiki is best understood as a generic label for community-maintained onion link directories, not a single authoritative service. It’s frequently referenced as a way people “find” dark websites. Still, it has a long history of forks, mirrors, impersonations, and linkage to harmful/illegal material, making it unsuitable as a trusted or “legit” recommendation.
Important limitation (detail unspecified): Because there is no single official Hidden Wiki and many clones exist, an official onion address cannot be verified from a primary/official source. Accordingly, no onion address is provided in this post.
Best for: Discovering onion site categories.
3. Proton Mail (Encrypted Communication)
Proton Mail maintains an onion site to provide an additional layer of protection for users who prioritize confidential communication. The service is known for strong encryption and minimal data collection.
Its Presence on the Dark Web demonstrates that legitimate dark web sites can enhance digital privacy rather than enable wrongdoing.
A mainstream encrypted email provider that publishes an official onion site for users who need an extra layer of network-level privacy in high-risk situations. This is one of the clearest examples of a legit dark web site because it mirrors a typical consumer service while explicitly emphasizing privacy.
Verified onion Presence: protonmailrmez3lotccipshtkleegetolb73fuirgj7r4o4vfu7ozyd.onion (published on the provider’s Tor page).
Best for: Secure, encrypted email access.
4. ProPublica (Investigative Journalism)
ProPublica was among the first major news organizations to launch a Tor-accessible site. Its onion service helps readers bypass censorship and allows sources to share sensitive information more safely.
This makes it one of the more famous dark web sites, proving that the network is not solely associated with cybercrime.
A public-interest investigative newsroom that operates an onion mirror of its reporting, explicitly to improve secure/anonymous access. This is a strong reference point for readers because it frames the dark web as a channel for journalism and accessibility, rather than solely criminality.
Verified onion Presence: p53lf57qovyuvwsc6xnrppyply3vtqm7l6pcobkmyqsiofyeznfu5uqd.onion (published by the newsroom).
Best for: Independent investigative reporting.
5. SecureDrop (Whistleblower Protection)
SecureDrop is widely used by media organizations to receive confidential documents from whistleblowers. It is designed with anonymity in mind and supports secure file transfers without exposing a source’s identity.
Platforms like this illustrate how some onion sites on the dark web exist specifically to protect public-interest communication.
An open-source whistleblower submission ecosystem run for newsrooms and NGOs; its directory helps locate legitimate public-interest SecureDrop instances. Unlike random link lists, this directory is curated around verified organisations and includes prominent warnings about anonymity and security posture.
Verified onion Presence: sdolvtfhatvsysc6l34d65ymdwxcujausv7k5jk4cy5ttzhjoi6fzvyd.onion (published in the directory’s footer).
Best for: Anonymous document submission.
6. Facebook (Tor Mirror)
Facebook operates a mirror onion site that allows people to access the platform in regions where it may be restricted. It also helps users avoid certain surveillance risks tied to traditional connections.
Its scale alone makes it one of the most popular dark web sites, highlighting how mainstream companies sometimes use Tor to improve accessibility.
A major social platform with a long-running history of Tor onion access, often discussed in the context of censorship circumvention and safer access without leaving the Tor network. For readers, it’s best treated as an example of institutional onion presence rather than a discovery method for dark web content.
Verified onion presence (partial): A Tor Project blog post references the historic onion service name facebookcorewwwi. onion.
Important limitation (detail unspecified): During this research run (11 Feb 2026), Facebook/Meta primary pages that reportedly publish the current v3 onion address were not reliably accessible from the research environment (rate limiting/blocked access). As a result, the up-to-date onion address cannot be confirmed here from a primary/official Meta source.
Best for: Secure social media access in restricted environments.
7. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Official Onion Site
The CIA launched an official onion service to enable anonymous communication and provide global access to its information. While unexpected to some, it reflects growing institutional recognition of privacy technologies.
As a result, it is frequently cited among famous dark web sites that demonstrate the legitimate side of the network.
A government example of a mainstream institution offering an official Tor-accessible presence for secure, anonymous browsing of public content and contact pathways. It’s a useful legitimacy signal in a list like this because it demonstrates that onion services can be used for accessibility and anonymity, not just underground markets.
Verified onion Presence: ciadotgov4sjwlzihbbgxnqg3xiyrg7so2r2o3lt5wz5ypk4sxyjstad.onion (published by the agency).
Best for: Secure access to public agency information.
Onion-presence verification workflow

Why These Dark Web Sites Matter
A carefully curated list of dark websites reveals an important reality: the dark web is not inherently malicious. Many services focus on privacy, free expression, and secure communication.
Key takeaways:
- Not all onion services are dangerous.
- Reputable organizations operate several.
- Privacy technology has legitimate global uses.
- Critical thinking is essential when evaluating links.
Understanding this balance helps separate myth from reality while supporting safer, research-driven exploration.
A list of dark web sites typically includes privacy-focused search engines, investigative news platforms, encrypted communication tools, whistleblower systems, and censorship-resistant services. These onion sites demonstrate how the dark web enables anonymity and access to information beyond traditional internet infrastructure.
How to Access Dark Web Sites Safely
To access dark web sites, users typically use the Tor browser, which connects to the Tor network and enables access to .onion domains. However, accessing the dark web carries risks, including malware, scams, and surveillance, so strong cybersecurity practices and informed browsing habits are essential for safer research and learning.

What You Need to Access Dark Web Sites
Understanding the basics is the first step before researching this part of the internet. Educational awareness, not experimentation, should guide your approach.
Tor Browser Overview
The most commonly referenced dark web site browser is the Tor Browser. It routes internet traffic through multiple encrypted relays, helping reduce direct traceability between the user and the destination.
When people discuss Tor browser dark web sites, they are usually referring to websites designed to operate within this privacy-focused network rather than the traditional web.
Onion Domains Explained
Instead of standard domains like .com or .org, dark web sites often use .onion addresses. These domains:
- Are not indexed by traditional search engines
- Require compatible privacy browsers
- Change more frequently than surface web domains
Because onion addresses can be complex and temporary, users often rely on dark web search engines or curated directories for academic or cybersecurity research.
Risks of Accessing Dark Web Sites
Before learning how to find dark web sites, it is critical to understand the environment. The dark web is less regulated than the surface web, which increases exposure to security threats.
Malware: Some pages attempt to deliver malicious files that can compromise devices or steal information.
Fake Sites: Impersonation is common. Fraudulent clones may mimic legitimate services to capture credentials.
Scams: Financial fraud, deceptive services, and misinformation appear more frequently in anonymous ecosystems.
Awareness of these risks helps frame access as a cybersecurity topic rather than a casual browsing activity.
Cybersecurity Precautions
If you are studying how to search dark web sites from an educational or professional perspective, protective habits are essential.
Use Privacy Tools Thoughtfully
Some security professionals recommend layered privacy strategies. A VPN is sometimes discussed in cybersecurity contexts as an additional privacy measure. Still, practices vary depending on organizational policies and threat models.
Avoid Downloads
Downloading files from unknown sources significantly increases the risk of exposure.
Verify URLs Carefully
Onion addresses are sensitive to even small character changes. Always treat unfamiliar links with caution and rely on reputable research sources whenever possible.
Maintain a Security Mindset
Keep software up to date, use strong authentication, and avoid sharing personal information in anonymous environments.
Common Misconceptions
Accessing the dark web is illegal.
In most regions, simply accessing dark web infrastructure is not illegal. Legal concerns arise from activities conducted there, not from the technology itself.
Everything on the dark web is criminal.
While some spaces are associated with cybercrime, others support journalism, privacy advocacy, academic research, and secure communication.
Anonymity means complete safety.
Privacy tools reduce traceability but do not eliminate risk. Responsible behavior remains the strongest defense.
Learning how to access dark web sites should always be approached with awareness and cybersecurity in mind. The goal is to understand how privacy technologies work, recognize potential threats, and develop safer digital habits that avoid anonymous environments for risky behavior.
When framed correctly, the topic becomes less about mystery and more about digital literacy in an evolving internet landscape.
Is It Illegal to Visit Dark Web Sites?
No, visiting dark web sites is not illegal in most countries. However, participating in illegal activities while on the dark web is against the law. The legality depends on user actions, not simply accessing the network.

Is Accessing the Dark Web Legal?
In general, accessing the dark web itself is legal in many jurisdictions. Privacy-focused tools such as the Tor network were originally developed to enhance secure communication, not to enable criminal activity.
When people ask, “Is it illegal to visit dark websites?” the answer is that access alone is usually not a crime. What matters is how the network is used.
That said, laws vary by country, and local regulations should always be reviewed. Some governments restrict anonymity tools or monitor usage more closely than others.
What Makes Activity Illegal?
The legal line is crossed when someone engages in unlawful behavior, not when they load a page.
Illegal activity may include:
- Purchasing prohibited goods
- Selling stolen data
- Participating in fraud or hacking schemes
- Distributing illegal content
The technology itself is neutral. Criminal intent or actions determine liability. Even on the surface web, illegal actions remain illegal; the same principle applies here.
Understanding this distinction helps separate curiosity from compliance.
Countries With Restrictions
While most democratic nations allow access to privacy networks, some countries impose stricter controls. In certain regions:
- Anonymity tools may be restricted or monitored
- Access to specific sites may be blocked
- Using encryption without authorization could raise legal concerns
Before exploring privacy technologies, individuals should review applicable laws in their jurisdiction. Legal standards differ significantly across borders.
Legal vs Illegal Dark Web Sites
Not all dark web sites are criminal. In fact, many operate for legitimate purposes.
Examples of Legal Dark Web Sites
- Investigative journalism platforms
- Whistleblower submission systems
- Privacy-focused communication services
- Academic or research archives
These are often considered legal dark web sites because their purpose aligns with lawful communication and information access.
Identifying Safe and Legitimate Services
Users looking for safe dark web sites or legit dark web sites should evaluate:
- Transparency of the organization
- Clear mission or public purpose
- Established reputation
- Security-focused design
Be cautious about fake dark web sites that may impersonate legitimate services to steal credentials or distribute malware.
If you encounter suspicious or harmful activity, many cybersecurity organizations guide reporting dark web sites involved in scams or criminal activity.
Is it illegal to visit dark web sites? Usually, no, but legality depends entirely on user behavior. Accessing privacy infrastructure is not the same as engaging in unlawful conduct.
Approach the topic with awareness, understand local laws, and prioritize cybersecurity and responsible use.
Dark Web Data Leak Sites: What They Are and Why They Matter
Dark web data leak sites are platforms where stolen databases, ransomware leaks, and exposed personal information are published or referenced. Cybersecurity professionals monitor these spaces to identify breaches early, understand attacker behavior, and reduce organizational risk before stolen data spreads further.

What Are Data Leak Sites?
Dark web data leak sites are online platforms where threat actors publicize compromised information, often to pressure victims, build a reputation, or signal responsibility for a cyberattack. These sites typically appear after a security breach and may contain samples of stolen records as proof.
From a threat-intelligence perspective, they function as early warning signals rather than destinations for legitimate browsing. Security teams analyze them to understand:
- The scale of a breach
- Types of data exposed
- Industries being targeted
- Emerging attack patterns
It is important to distinguish these platforms from privacy-driven spaces such as dark web news sites, dark web blog sites, or dark web education sites, which exist to support anonymous communication and public-interest reporting rather than exploit stolen data.
Ransomware Leak Sites Explained
Ransomware groups increasingly operate dedicated leak portals. When a victim refuses to pay, attackers may threaten to publish sensitive files, a tactic often called double extortion.
Typical characteristics include:
- Timed disclosure warnings
- Company name listings
- Negotiation pressure
- Partial data previews
For defenders, these portals provide insight into attacker strategy. Monitoring them helps organizations respond faster, notify affected parties, and strengthen defenses before further damage occurs.
Understanding ransomware leak behavior is now considered a core component of modern cybersecurity intelligence.
Why Businesses Monitor the Dark Web
Organizations do not monitor the dark web out of curiosity; they do so to detect and protect against risks.
Security teams watch dark web data leak sites to:
- Detect exposed employee credentials
- Identify leaked customer records
- Track brand impersonation
- Anticipate regulatory exposure
- Support incident response
Early detection can significantly reduce financial, operational, and reputational harm.
It is equally important to recognize that not every anonymous platform is malicious. Dark web forums and chat sites sometimes support privacy-focused discussions, research collaboration, or secure communication. Context matters, and cybersecurity analysis focuses on threat indicators rather than broad assumptions.
How Organizations Protect Themselves
Because data leaks often originate from preventable weaknesses, proactive security remains the strongest defense.
Leading organizations typically prioritize:
Continuous Threat Monitoring: Specialized intelligence services scan for indicators of compromise across dark web environments.
Strong Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication and least-privilege policies reduce the chance of credential abuse.
Employee Security Awareness: Human error remains a major vector for breaches. Training helps staff recognize phishing and social engineering attempts.
Encryption and Data Governance: Protecting sensitive data limits the value of information even if attackers gain access.
Incident Response Planning: Prepared organizations react faster, minimizing disruption and regulatory impact.
Dark web data leak sites have become a critical signal in the cybersecurity landscape. While they represent real risk, they also provide valuable intelligence that helps defenders understand threats and respond more effectively.
For modern organizations, awareness is no longer optional; it is a strategic requirement. Monitoring emerging threats, strengthening internal controls, and maintaining a proactive security posture can turn potential crises into manageable incidents.
Are Legal Dark Web Sites Safe?
Legal dark web sites can offer valuable privacy protections, but their legality does not automatically make them risk-free. Even reputable platforms operate within anonymous networks where malicious actors may attempt to impersonate users, engage in phishing, or distribute malware. Understanding this distinction is essential for safer, informed browsing.

One common misconception is that if a service is lawful, it must also be completely secure. In reality, the infrastructure that supports anonymity can attract both legitimate organizations and cyber threats. This is why cybersecurity professionals emphasize caution, not fear, when interacting with any dark web environment.
Key Risks to Be Aware Of
Malware Exposure
Some fraudulent pages disguise themselves as trusted services to deliver harmful software. A single unsafe download can compromise devices or sensitive data.
Cloned or Fake Sites
Attackers sometimes replicate well-known platforms using nearly identical onion addresses. Without careful attention, users may unknowingly enter credentials into a fake portal.
Phishing Attempts
Anonymous ecosystems can make it harder to verify identity, increasing the likelihood of deceptive messages or login requests.
Why Verification Matters
Before trusting any platform, take time to confirm its legitimacy. Look for signs such as:
- Official references from recognized organizations
- Consistent domain information
- Established public reputation
- Security-focused design
Verification is one of the most effective ways to reduce risk while navigating privacy-focused networks.
The Balanced Perspective
Legal dark web sites play an important role in supporting journalism, research, secure communication, and freedom of information. However, safety ultimately depends on user awareness and responsible digital behavior.
The smartest approach is to treat the dark web with the same cybersecurity mindset you would apply anywhere online: stay alert, verify sources, avoid unnecessary downloads, and prioritize trusted platforms.
How to Identify Legit Dark Web Sites
Knowing how to identify legit dark web sites is essential for reducing security risks and avoiding scams. Because anonymous networks lack the same visibility as the surface web, users must rely on credibility signals rather than assumptions. A careful verification process helps separate trustworthy platforms from deceptive ones.
Look for Verified Organizations
The safest dark web services are typically operated by recognized institutions such as established media outlets, privacy-focused technology providers, academic projects, or public-interest organizations. If a platform openly connects to a real-world entity with a documented mission, its legitimacy is easier to evaluate.
Check Security Signals
While onion services differ from traditional websites, strong platforms still prioritize security. Indicators may include:
- Clear privacy policies
- Transparent purpose
- Professional interface
- Consistent domain usage
- Public documentation explaining the service
These signals suggest that the site prioritizes user protection over exploitation.
Avoid Cloned Onion Domains
One of the most common threats involves cloned websites designed to imitate trusted services. Even a minor character difference in an onion address can redirect users to a fraudulent page.
To reduce this risk:
- Use official sources when locating domain addresses
- Avoid clicking on unknown directories
- Treat unsolicited links with caution
Accuracy matters, especially in anonymous environments.
Evaluate Reputation Carefully
Reputation serves as a powerful indicator of trust. Legitimate platforms are often referenced in cybersecurity research, academic discussions, or reputable technology publications.
Consider whether the service has:
- Independent mentions from trusted sources
- A history of stable operation
- Clear organizational backing
If reliable information is difficult to find, caution is the safer choice.
Security-First Mindset
Identifying legitimate services is less about technical expertise and more about disciplined digital behavior. Verification, patience, and critical thinking significantly reduce exposure to fraudulent platforms.
In privacy-focused networks, trust should always be earned, never assumed.
Legal vs Criminal Dark Web Infrastructure
Understanding the difference between lawful platforms and criminal networks is essential for navigating anonymous environments responsibly. While many legal dark web sites exist to support privacy, journalism, and secure communication, criminal infrastructure is typically designed to exploit anonymity for financial gain or data theft. Recognizing this contrast strengthens cybersecurity awareness and helps users make safer decisions.

Purpose and Intent
Legal platforms usually operate with a clear mission, such as protecting free expression, enabling confidential reporting, or supporting research. Their goals are transparent and aligned with lawful digital activity.
Criminal infrastructure, by contrast, often focuses on monetizing stolen information, conducting fraud, or pressuring victims after cyberattacks. For example, dark web data leak sites are commonly used to publicize compromised databases. In contrast, ransomware leak sites on dark web portals may threaten organizations with data exposure to force payment.
Transparency vs Anonymity Abuse
Legitimate services typically maintain some form of public accountability, even when protecting user privacy. They may be backed by known organizations or referenced by reputable institutions.
Criminal platforms tend to conceal ownership entirely and shift locations frequently to avoid enforcement. The Presence of impersonation tactics and dark web scam sites further illustrates how anonymity can be misused to deceive visitors.
Risk Profile
Legal sites generally emphasize secure communication and user protection. However, criminal environments pose significantly higher risks, including exposure to malware, financial fraud, and identity theft.
A helpful way to view the distinction:
| Factor | Legal Infrastructure | Criminal Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Privacy, information access | Profit through exploitation |
| Organizational Presence | Often associated with real entities | Typically hidden |
| Security Approach | Designed to protect users | Often designed to target them |
| Risk Level | Moderate | High |
Why This Distinction Matters
For cybersecurity professionals and everyday users alike, recognizing infrastructure types enables smarter risk assessment. Monitoring threat ecosystems, including dark web data leak sites, helps organizations anticipate breaches. At the same time, understanding scam patterns reduces the likelihood of falling victim to fraud.
The key takeaway is that the dark web itself is not inherently illegal; it is a technological environment used for both constructive and harmful purposes. Awareness of the difference allows individuals and businesses to approach privacy networks with clarity rather than assumption.
Why Dark Web Sites Are Seized or Shut Down
Dark websites are sometimes seized or shut down when authorities identify serious violations of the law. While anonymity networks support legitimate privacy use cases, they are not beyond regulation. Law enforcement agencies worldwide actively investigate criminal activity and dismantle platforms that pose a significant public risk.

Understanding why these shutdowns occur helps clarify an important point: the technology itself is neutral, but unlawful behavior invites enforcement.
Law Enforcement Operations
Cybercrime investigations often involve international cooperation between agencies. Because many dark web operations cross borders, coordinated efforts allow investigators to track infrastructure, gather digital evidence, and disrupt illegal networks.
When a site is seized, visitors may see a notice indicating that authorities have taken control, a visible reminder that anonymous platforms are still subject to legal oversight.
Illegal Marketplaces
One of the most common reasons for a shutdown involves marketplaces facilitating the sale of prohibited goods or services. These platforms typically attract sustained investigative attention due to their scale and potential harm.
Their removal demonstrates that even highly concealed systems can eventually be uncovered through advanced forensic techniques and intelligence work.
Fraud Networks
Fraud-driven ecosystems, including phishing hubs, impersonation services, and some dark web scam sites, are also frequent targets of enforcement. These operations often rely on deception to exploit users, making them a priority for cybersecurity and financial crime units.
Authorities may also intervene when platforms are linked to broader threat activity, such as dark web data leak sites or ransomware leak sites, dark web environments that pressure organizations after breaches.
What This Means for Users
The existence of seizures highlights a critical distinction: not all dark web sites operate outside the law. Many privacy-focused platforms remain active because their purpose aligns with legal communication and information sharing.
For users, the takeaway is awareness. Enforcement actions signal which behaviors cross legal boundaries and reinforce the importance of engaging only with reputable, lawful services.
In an evolving threat landscape, shutdowns are less about the technology itself and more about maintaining accountability in digital spaces.
Are There Completely Safe Dark Web Sites?
No dark website is completely risk-free. Even legal platforms operate in anonymous environments where malicious actors may attempt scams, impersonation, or the distribution of malware. However, reputable organizations significantly reduce risk by implementing strong security practices, transparent operations, and privacy-focused infrastructure.
Why Safe Doesn’t Mean Risk-Free
The dark web is designed to enhance anonymity, which benefits journalists, researchers, and privacy advocates. Still, the same anonymity can also attract cyber threats. This means that even well-established services must be approached with awareness rather than blind trust.
Risk does not automatically indicate illegitimacy. Instead, it reflects the broader environment in which these platforms operate.
What Makes Some Dark Web Sites Safer Than Others?
While absolute safety does not exist online, certain characteristics signal stronger protection:
- Operated by recognized organizations
- Clear mission and public accountability
- Security-first design
- Verified onion domains
- Positive reputation in cybersecurity circles
These factors help distinguish trustworthy platforms from deceptive ones.
The Smart User Mindset
Instead of asking whether a site is perfectly safe, a better question is whether it demonstrates credibility and responsible security practices. Applying the same caution used across the internet, verifying sources, avoiding unknown downloads, and staying alert to impersonation, greatly reduces exposure to threats.
Safety on the dark web is not about certainty; it is about informed judgment. Awareness, verification, and cybersecurity discipline remain the strongest defenses in any anonymous digital space.
Who Should Actually Use Legal Dark Web Sites?
Legal dark websites are not designed for casual browsing or curiosity-driven exploration. Instead, they serve specific professional and privacy-focused needs where secure communication and reduced traceability are essential. Understanding the intended audience helps reinforce responsible use while strengthening cybersecurity awareness.
Journalists
Investigative reporters often rely on anonymous channels to communicate with confidential sources. Legal dark web platforms can help protect whistleblowers, reduce surveillance risks, and support sensitive reporting, particularly in environments where press freedom is limited.
Researchers
Academic and policy researchers sometimes study anonymous networks to understand better digital behavior, privacy technologies, and emerging cyber threats. Accessing legal platforms allows them to gather insights without compromising ethical standards.
Cybersecurity Teams
Security professionals monitor parts of the dark web to track threat indicators, analyze attacker tactics, and identify potential data exposure. Observing environments such as dark web data leak sites can help organizations respond more quickly to breaches and strengthen their defensive strategies.
Activists and Privacy Advocates
Individuals working in high-risk regions may use privacy-focused services to communicate safely and share information without fear of retaliation. For many, anonymity is less about secrecy and more about personal protection.
A Professional Tool, Not a Casual Destination
The key takeaway is that legal dark web sites function best as specialized tools. When used responsibly by professionals with a clear purpose, they support secure communication, research, and public-interest work.
Rather than asking who can use these platforms, the better question is who needs them. In most cases, value comes from informed, intentional use, not passive browsing.
The Growing Role of the Dark Web in Cybersecurity Monitoring
The dark web has evolved into a critical intelligence layer for modern cybersecurity. What was once viewed primarily as a hidden corner of the internet is now actively analyzed by security teams to identify threats, detect breaches early, and strengthen organizational defenses. Monitoring these environments allows defenders to move from reactive response to proactive protection.

Why the Dark Web Matters for Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence focuses on understanding risks before they escalate. Many cyber incidents leave early signals in anonymous networks, giving organizations a valuable window to respond.
Security teams often monitor:
- Dark web leaked data sites where compromised credentials or databases may surface
- Discussions indicating planned attacks
- Mentions of corporate systems or vulnerabilities
- Emerging tactics used by threat actors
These insights help organizations anticipate risks rather than discover them after damage occurs.
Strengthening Breach Detection
One of the most practical benefits of dark web monitoring is faster breach detection. Stolen information may appear online weeks or even months before a company realizes an incident has occurred.
Early discovery enables organizations to:
- Reset exposed credentials
- Notify affected users
- Investigate intrusion points
- Reduce regulatory and reputational impact
In many cases, timing determines whether a breach becomes manageable or catastrophic.
From Reactive Security to Predictive Defense
Cybersecurity strategies are increasingly intelligence-driven. Instead of relying solely on internal system alerts, organizations combine network monitoring with external visibility.
This shift supports:
- Better risk forecasting
- Improved incident response planning
- More informed security investments
- Stronger executive decision-making
The result is a more resilient security posture built on awareness rather than assumption.
Not All Dark Web Activity Signals Criminal Intent
It is equally important to maintain perspective. Anonymous networks also host privacy-focused communities, research discussions, and secure communication channels. Cybersecurity professionals analyze these environments carefully, focusing on threat indicators rather than drawing broad conclusions.
This balanced approach reinforces credibility, a key factor for organizations building mature security programs.
The growing role of the dark web in cybersecurity monitoring reflects a larger shift in how organizations manage risk. Visibility beyond traditional networks is no longer optional; it is a strategic advantage.
By integrating threat intelligence with breach detection capabilities, businesses can identify warning signs earlier, respond faster, and operate with greater confidence in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Legal vs Illegal Dark Web Sites: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between legal and illegal platforms is essential for safer navigation and stronger cybersecurity awareness. While many dark web services support privacy and free expression, others operate solely for exploitation. The table below highlights the core distinctions.
| Factor | Legal Dark Web Sites | Illegal Dark Web Sites |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Privacy protection, journalism, research, secure communication | Criminal profit, fraud, stolen data distribution |
| Transparency | Often connected to known organizations or public missions | Hidden operators with little to no accountability |
| Risk Level | Moderate — still requires caution | Very high — increased exposure to scams, malware, and legal consequences |
Why This Comparison Matters
Not all dark web platforms carry the same level of risk. Recognizing intent, transparency, and operational behavior helps users distinguish trustworthy services from dangerous ones.
Legal platforms typically prioritize user safety and ethical communication. In contrast, illegal environments often intersect with threats such as dark web leaked data sites or organized fraud networks.
Legal dark web sites usually support privacy, journalism, and secure communication. In contrast, illegal sites focus on criminal activity and financial gain. The biggest differences lie in transparency, purpose, and risk, making careful evaluation essential before trusting any anonymous platform.
Conclusion
The dark web is often shrouded in mystery. Still, in reality, it is simply another layer of the internet, one that prioritizes privacy and anonymity. While some dark web sites support legitimate purposes such as journalism, research, secure communication, and threat intelligence, others are linked to scams, data leaks, and cybercrime. Understanding this balance is essential for making informed decisions.
As cybersecurity risks continue to evolve, awareness has become more important than ever. Organizations now monitor dark web environments to detect breaches earlier. At the same time, professionals use privacy-focused platforms to protect sensitive information and sources.
The key takeaway is not to view the dark web with automatic fear or blind trust, but with informed caution. By recognizing the distinction between legal and criminal infrastructure, carefully verifying platforms, and maintaining strong cybersecurity habits, users can approach this hidden part of the internet with greater confidence and responsibility.
Ultimately, knowledge is the strongest defense. The more you understand how dark web sites operate, the better prepared you are to navigate today’stoday’somplex digital landscape safely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Is it illegal to visit dark web sites?
No, visiting dark web sites is not illegal in most countries. What determines legality is user behavior, not access to the network itself. Activities such as fraud, purchasing illegal goods, or distributing harmful content remain unlawful regardless of where they occur online.
Are there legal dark web sites?
Yes, many legal dark web sites exist and serve legitimate purposes. These include investigative journalism platforms, encrypted communication services, whistleblower systems, and research resources. Such platforms use anonymity to protect users and support secure information sharing rather than facilitate criminal activity.
Are dark web sites dangerous?
Some dark web sites can present security risks, including scams, phishing attempts, malware, and exposure to leaked data. However, not every platform is harmful. Understanding how to identify reputable services and practicing strong cybersecurity habits can significantly reduce the risk of threats.
What are dark web sites used for?
Dark web sites are commonly used for privacy-focused communication, anonymous reporting, academic research, and bypassing censorship in restricted regions. While these legitimate uses exist, the same infrastructure can also attract cybercrime, making awareness and careful evaluation essential.
Can you access dark web sites safely?
Accessing dark web sites carries inherent risk, but safer practices can help reduce exposure. Using trusted privacy tools, verifying onion addresses from official sources, avoiding downloads, and keeping security software up to date are all important steps for responsible research.
How do you identify legit dark web sites?
Recognized organizations typically operate legitimate dark websites, have a clear mission, and are referenced by credible sources. Checking official announcements, confirming domain accuracy, and avoiding cloned sites are effective ways to distinguish trustworthy platforms from fraudulent ones.
Why do cybersecurity teams monitor the dark web?
Cybersecurity professionals monitor the dark web to detect stolen credentials, identify emerging threats, and respond to potential breaches earlier. Observing environments such as data leak platforms provides threat intelligence that helps organizations strengthen defenses and minimize operational damage.
Are there completely safe dark web sites?
No dark web site is completely risk-free. Even legal platforms operate within anonymous networks where malicious actors may attempt to impersonate or commit fraud. However, reputable organizations reduce risk through strong security practices, transparent operations, and privacy-focused infrastructure.