The digital shadow known as the dark web fascinates, frightens, and mystifies millions, and with good reason. In this guide, I’ll take you well beyond headlines and sensational myths to explain how this hidden layer of the internet really works, why it matters for individuals and organizations, and practical steps you can take to stay safe. Expect clear, evidence-based explanations, actionable advice, and no unnecessary technical fluff.
What is the dark web? A clear definition for anyone
The simplest way to think about the dark web is that it’s a subset of the internet intentionally hidden from standard search engines and casual browsers. It sits beneath the surface web (the content indexed by Google) and the deeper web (remote databases, behind-login pages). Unlike sites you access with a standard browser, dark web sites often require specialized software and network configurations to access. This architecture provides strong privacy protections and, at times, shelter for illicit activity.
How the dark web works: networks, anonymity, and access
Tor I2P and the mechanics of privacy
Most users reach the hidden internet through anonymity networks. Tor is the most widely known: it routes traffic through multiple volunteer-run relays so that neither the sender nor the receiver is easily traceable. I2P and other overlay networks apply similar onion-routing concepts with different tradeoffs in speed and persistence.
Hidden services and addressing
Instead of regular domain names, many hidden sites use cryptographic addresses that aren’t indexed by conventional search engines. That obscurity is both a strength and a weakness: it can protect dissidents and whistleblowers in repressive regimes, but it also makes illicit marketplaces harder to police.
Myths vs reality: common misconceptions about hidden online spaces
- Myth: Everything on the unlit web is illegal.
- Reality: Many legitimate uses exist: secure communication for journalists, privacy-focused communities, research, and circumvention of censorship.
- Myth: Using the dark web automatically makes you a target.
- Reality: Risk varies by activity. Passive browsing is different from participating in markets or downloading unknown files.
- Myth: Law enforcement can’t touch anything there.
- Reality: Agencies have disrupted marketplaces and made arrests using targeted operations, infiltration, and digital forensics.
How criminals operate on hidden networks: tactics and trends
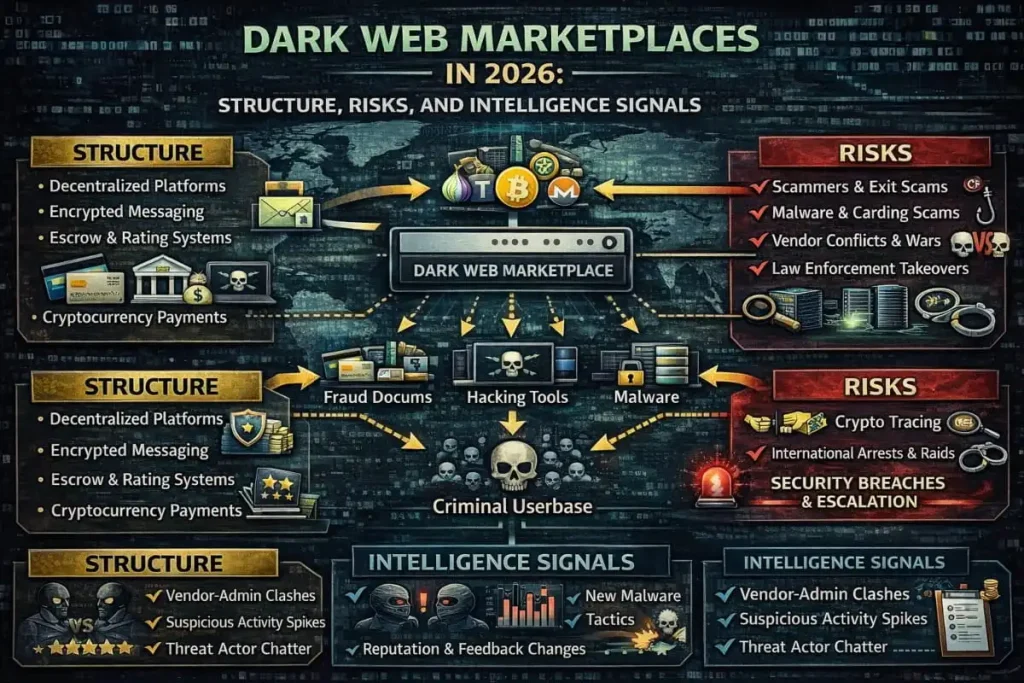
Understanding typical threats is essential for strong Digital Risk Protection. Key illicit activities include stolen data markets, malware-as-a-service, and fraud forums. These services are often supported by reputation systems, escrow mechanisms, and vendor feedback systems similar to those of legitimate e-commerce marketplaces.
- Data trafficking: Compromised credentials and personal data are packaged and sold. This feeds identity theft and account takeover.
- Malware & services: Ransomware groups, botnet operators, and phishing-as-a-service vendors coordinate operations and trade tools.
- Forums & intelligence sharing: Actors exchange techniques, test vulnerabilities, and trade access to corporate networks.
Why the dark web matters for you and your organization
Even if you never visit a hidden site, the consequences reach far beyond its bounds. Stolen credentials sold there can unlock personal accounts, corporate systems, and financial services. For small businesses and enterprises alike, a single leaked database can cause reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and costly incident response.
Detecting exposure: scans, reports, and monitoring explained
Organizations and individuals can detect exposure by combining automated scans, intelligence feeds, and manual investigation.
- Dark Web Scan tools crawl adversary markets and paste sites to locate leaked credentials and sensitive data.
- A Darkweb report summarizes findings, risk level, and recommended remediation steps after an investigation.
- Dark Web breach Monitoring provides continuous alerts for newly discovered data tied to your domain, brand, or personal emails.
Each of the terms above refers to capabilities available from vendors and open-source projects. Choosing the right mix relies on budget and needs.
Hands-on protection: practical steps anyone can follow
Here’s a concise, prioritized checklist you can use immediately:
- Use unique, strong passwords and a reputable password manager.
- Enable multi-factor authentication on all accounts that support it.
- Run periodic scans to check if email is compromised and change credentials for affected accounts.
- Keep devices and software up to date to patch common exploit vectors.
- Avoid reusing corporate credentials on personal services or vice versa.
Tools and tactics: selecting monitoring and response options
Many organizations use a layered approach:
Monitoring and response options at a glance
| Category | Typical Capabilities | Free Option? | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic email checks | Scan public breaches for email addresses | Some free Dark Web Monitoring tools exist | Individuals & small businesses |
| Continuous breach monitoring | 24/7 alerts for brand, domain, or email exposure | Usually paid | Enterprises, SOC teams |
| Manual intelligence collection | Targeted searches, forum monitoring, Open Source Intelligence collection | Free but labor-intensive | Security researchers |
| Forensic investigations | Deep Darkweb report with context and attribution | Paid | Incident response teams |
| Automated remediation | Password resets, MFA enforcement, account lockouts | Paid integrations | Large orgs / MSSPs |
Free vs paid solutions: when to upgrade
- Free tools are helpful for spot checks and personal use. They can tell you if an email appears in public dumps or pastes, but they often lack continuous coverage and deep context.
- Paid Dark Web Monitoring tools typically provide broader visibility, higher-quality enrichment (who exposed the data and where it appears), and integration with security stacks for automated responses.
If you’re a small business, start with free checks to assess baseline risk; upgrade when exposure becomes frequent or sensitive data is involved.
Using Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) and cyber threat intelligence effectively
Combining Open Source Intelligence with Cyber threat intelligence enhances context. OSINT helps locate mentions of your organization or personnel across forums, paste sites, and social platforms. Cyber threat intelligence enriches those findings with indicators of compromise, attacker TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures), and recommended mitigations. Together, they reduce false positives and accelerate response.
How to run a darkweb search safely and legally
A targeted darkweb search involves scanning relevant marketplaces, forums, and dump sites for your organization’s domain names, brand names, or employee email addresses. Best practices:
- Use a secure, isolated environment (air-gapped or VM) for investigations.
- Never interact or transact on illicit marketplaces. Collect only observable data.
- Maintain legal counsel and follow local laws when conducting active research.
Response playbook: what to do if your data appears in a leak
If a scan or Dark Web email scan shows exposure, act immediately:

- Contain: Reset affected credentials and enforce MFA.
- Assess: Use a Darkweb report or forensic analysis to understand what leaked (passwords, financial details, PII).
- Notify: Inform affected stakeholders and regulators where required by law.
- Remediate: Patch vulnerabilities, rotate secrets, and tighten logging/monitoring.
- Monitor: Increase Breaches Monitoring for related artifacts.
Which indicators are urgent? Signs you may be compromised
Look for these red flags:
- Unexplained logins from unfamiliar locations or devices.
- Multiple password reset attempts across services.
- Receipt of targeted phishing emails referencing internal details.
- Sudden appearance of company credentials in public paste sites or marketplaces.
If you see any of these, prioritize an investigation.
Privacy, ethics, and legal considerations
Researching the hidden web can expose investigators to illicit content and legal risk. Always:
- Follow applicable laws and company policies.
- Avoid downloading illegal material.
- Work with legal and compliance teams before acting on intelligence that could trigger mandatory breach notifications.
Building an organizational program: roles and responsibilities
A mature program typically involves:
- Security Operations (SOC): Continuous monitoring and triage.
- Incident Reaction: Containment, forensics, and remediation.
- Legal & Compliance: Notification obligations and regulatory reporting.
- Communications/PR: Transparent messaging for affected users and customers.
- HR & Identity teams: Managing compromised employee accounts and credential hygiene.
Free Dark Web Monitoring tools when they help
Free Dark Web Monitoring tools, along with other free services and community-maintained feeds, are valuable first steps. They can quickly tell you whether an email address has appeared in known dumps. However, they rarely offer the breadth, speed, or investigative depth of paid feeds. Use these free tools for initial detection and education, then move to paid monitoring if you require continuous coverage.
Case study snippets: what went wrong (and how it could have been prevented)
- Retail breach: A small retailer reused database credentials; attackers exfiltrated payment records that showed up on underground markets. Prevention: separate credentials, better secrets management, and continuous breach monitoring.
- Phishing campaign: Attackers used stolen employee emails to craft highly targeted messages, winning password resets. Prevention: mandatory MFA, phishing-resistant authentication, and user training.
Practical guide: how to check if your email is compromised (step-by-step)
- Use reputable services to check if email is compromised. Start with a free scan, then offer paid options for continuous monitoring.
- If found, change passwords, confirm 2FA is enabled, and review account activity.
- Consider a Dark Web Scan by a trusted security provider for deeper context.
How to choose the right Dark Web breach Monitoring provider
Scoring factors include:
- Coverage breadth (paste sites, closed forums, marketplaces)
- Speed of detection and alerting
- Context enrichment and actionable recommendations
- Integration with SIEM and incident response tools
- Data retention, reporting, and compliance support
Beyond monitoring: proactive defenses that matter
- Implement phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication.
- Rotate and manage secrets with a vault solution.
- Integrate identity threat detection (monitor for unusual authentication patterns).
- Regularly test backup integrity and disaster recovery plans.
The attacker’s economy: prices, trust systems, and marketplaces
Underground markets have matured: vendors earn reputations, buyers leave feedback, and services like escrow reduce fraud, all of which professionalize criminal activity. Understanding marketplace mechanics helps defenders anticipate where certain types of data might surface and why visibility matters.
Future trends: what will the hidden internet look like next?
Likely directions include stronger operational security by threat actors, more decentralized marketplaces, and greater use of privacy coins or mixing services for financial transactions. Defenders will respond with better automation, improved OSINT tooling, and a greater emphasis on identity-centric security and Brand Protection to limit exposure and reduce exploitation risks.
Quick reference, immediate steps if you suspect exposure
- Run an email check with a reputable scan.
- Reset passwords and enable MFA on affected accounts.
- Notify your security team and legal counsel.
- Begin a Darkweb report investigation if sensitive data is involved.
- Increase monitoring and document the incident response timeline.
Three short bullet lists for clarity
Top 6 defensive controls (practical):
- Multi-factor authentication (phishing-resistant where practicable)
- Unique passwords + password manager
- Least-privilege access and identity governance
- Continuous Breaches Monitoring and log alerting
- Patch management and endpoint protection
- Employee training and phishing simulations
Common signs of data exposure:
- Accounts receiving password resets you didn’t request
- Unexpected two-factor prompts or login alerts
- Emails referencing internal project names or records
When to escalate to incident response:
- PII or financial records are publicly listed
- Customer data appears on marketplaces.
- Evidence of active exploitation in your network
Building resilience: lessons for long-term security

Security is not a one-time project. The goal is to reduce risk through layered controls, continuous monitoring, and rapid reaction. Invest in people, processes, and technology, and ensure those investments are measured against real-world detections and outcomes.
Conclusion
The hidden internet presents both risks and protections. Understanding how it works, what actually happens there, and how to respond to exposure is where Cyber threat intelligence becomes essential, separating useful security programs from reactive panic. Whether you’re an individual checking an email or an enterprise building a monitoring program, a pragmatic, evidence-driven approach will keep you safer than fear-driven avoidance.
FAQs
What exactly is the dark web?
It’s a portion of the internet that’s not indexed by definitive search engines and often requires special software to access. It houses both legitimate privacy-focused services and illicit markets.
Can I check if my email has been leaked?
Yes, several reputable services and scans let you check breaches. If your address appears, change passwords, enable MFA, and monitor related accounts.
Are free Dark Web Monitoring tools useful?
They’re a good starting point for individuals or small businesses, but lack continuous, comprehensive coverage compared to paid solutions.
Will law enforcement investigate dark web leaks?
Sometimes investigations depend on the nature and scale of the crime, available evidence, and jurisdictional factors.
Should my company run a Dark Web Scan regularly?
Yes. Regular scanning and ongoing Dark Web breach Monitoring reduce detection lag and improve response times after a leak.