The Latest Data Breach has once again forced individuals and organizations to reassess how they protect personal and business data online. In an era where personal details, login credentials, and corporate secrets travel across networks and cloud services, a single breach can ripple outward, affecting financial security, reputation, and privacy for years. This post explains what the Latest Data Breach means for your digital safety, how attackers exploit exposed information, and the concrete steps you can take today to reduce risk and recover faster.
How data breaches actually put you at risk
A breach isn’t just a news headline it’s actionable fuel for attackers. When data is stolen, exposed, or sold, it becomes usable in multiple ways:
The attack chain: from breach to exploitation
- Stolen credentials lead to account takeover and fraudulent transactions.
- Personal data enables highly convincing phishing and social engineering.
- Collected metadata helps criminals build profiles for targeted scams.
Why scale and speed matter
Modern breaches release huge volumes of records that quickly circulate across forums and the Dark Web. That rapid distribution widens the window for attackers, making early Detection and response essential.
What was exposed: standard breach contents and their impact
Breaches typically include one or more of the following types of data, each with different consequences:
- Login credentials (usernames, emails, hashed or plain passwords) primary vector for account takeover.
- Contact information (emails, phone numbers, addresses) used for targeted phishing.
- Payment and financial data direct route to theft and fraud.
- Personal identifiers (national IDs, birthdates) long-term identity fraud risk.
- Internal corporate files intellectual property loss and regulatory exposure.
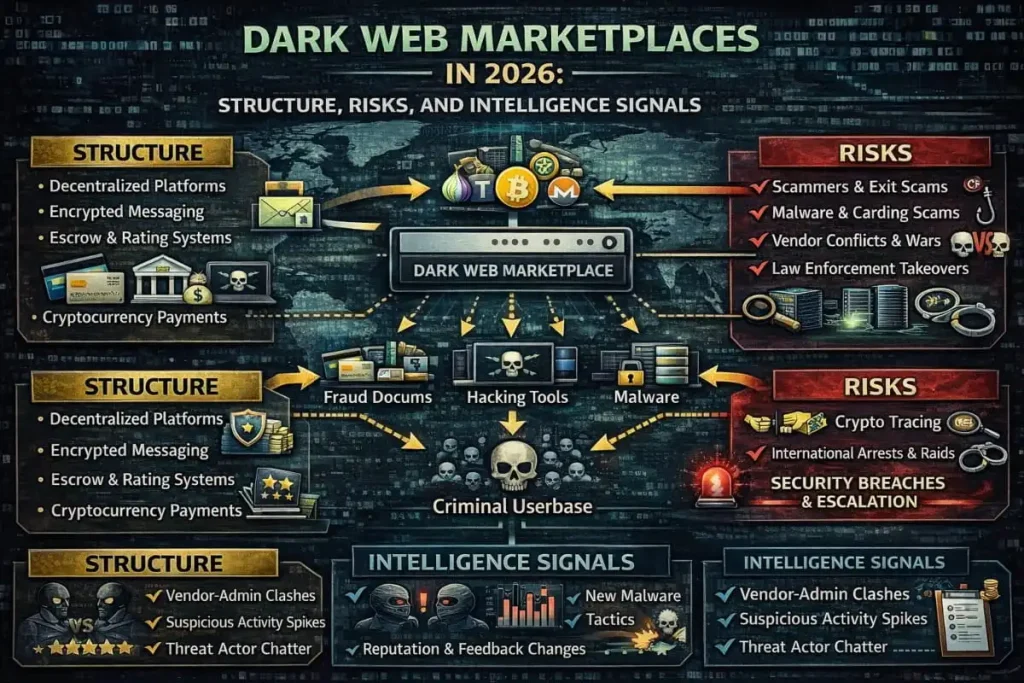
Understanding the attacker’s marketplace
Once breached, data moves through a market ecosystem: collectors, resellers, brokers, and end users. Criminals use automation and analytical tools to validate, aggregate, and weaponize datasets rapidly. With strong Digital risk protection, individuals and organizations can better detect and limit the circulation of this stolen information. This is why the presence of your information in one breach can quickly multiply into multiple attack vectors across platforms.
Detect early: monitoring and scanning you should know about
Early Detection reduces damage. Here are practical monitoring approaches that matter now.
Dark Web Monitoring and why it helps
Dark Web Monitoring scans relevant underground forums and marketplaces for mentions of stolen data tied to your email, domain, or company. When a match appears, security teams gain an early warning to act.
Deep Web Scanning for hidden exposures
Deep Web Scanning goes beyond indexed search engines to uncover exposed files and credentials in areas standard tools miss. It helps map where your sensitive assets may have leaked.
Email-focused scans: Email data breach scan and Email Dark Web Scan
Performing an Email data breach scan or an Email Dark Web Scan for your personal and business addresses finds whether credentials or contact lists tied to those addresses have shown up in breaches.
Immediate steps you must take right now
If you suspect exposure from a breach, prioritize these actions:
- Change the passwords on affected accounts and any accounts that use the same password.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) everywhere possible.
- Run an Email data breach scan or use the email data breach tool to identify broader exposure.
- Review recent account activity and freeze payments or cards if suspicious transactions appear.
- Practical tip: Use a reputable password manager to generate and store unique passwords it’s one of the fastest ways to cut risk from credential reuse.
A practical checklist for individuals and families
Below is a short checklist you can run through within 30–60 minutes after learning about an exposure:
- Confirm which accounts are affected.
- Reset passwords and secure primary email accounts first.
- Turn on MFA and review recovery options.
- Check bank/card accounts and set alerts for atypical activity.
- Run a one-time free dark web scan or get a Free Dark Web Report to see if your email or SSN appears in leaked data.
What organizations should do differently now?
Businesses face a higher regulatory and reputational burden. A breach is also an organizational problem requiring cross-functional coordination.
Rapid response actions for security teams
- Activate incident response and legal teams.
- Isolate and contain compromised systems immediately.
- Communicate transparently with affected customers and regulators.
- Deploy Breaches Monitoring to track where corporate data appears across channels.
- Longer-term defensive commitments
- Invest in layered controls: logging, network segmentation, and access controls.
- Implement Data Leak Prevention programs to stop data exfiltration.
- Adopt proactive Cyber Threat Analysis and threat-hunting practices to reduce dwell time.
The role of intelligence: proactive vs reactive defense
To stay ahead, organizations should marry Detection with intelligence.
Cyber threat intelligence and Real Time Threat Intelligence
Deploying Cyber threat intelligence sources and Real Time Threat Intelligence enables teams to correlate breach artifacts with active campaigns, improving prioritization and speeding containment.
Credentials Leak Detection at scale
Set up Credentials Leak Detection workflows that automatically flag reused credentials and require remediation, preventing attackers from exploiting exposed logins.
Table Immediate vs. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Actions
| Timeframe | Individual actions | Organizational actions | Tools to consider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate (Hours) | Change passwords; enable MFA; run Check email data breach | Contain systems; notify stakeholders; start forensic logs | Email data breach scan, account alerts |
| Short-term (Days) | Run free dark web scan; review financial statements | Patch systems; rotate keys; issue customer guidance | Dark Web Monitoring, Breaches Monitoring |
| Long-term (Weeks–Months) | Use password manager; enroll in ID monitoring | Deploy Data Leak Prevention, threat intelligence | Deep Web Scanning, Cyber Threat Analysis |
How to interpret a Darkweb report or Free Dark Web Report
A Darkweb report or Free Dark Web Report will usually show whether your identifiers (emails, phone numbers) surfaced in underground postings. Key things to look for:
- Date of appearance: newer entries are higher immediate risk.
- Type of data exposed: credentials and financial info are critical.
- Context: whether the data was dumped in bulk or targeted to a specific buyer.
If you see your information, treat the exposure as actionable not theoretical.
Common misconceptions that put you at more risk

Many people underestimate the impact of breaches due to myths. Let’s correct the most damaging ones:
- If it wasn’t credit card data, I m safe. Wrong. Credentials and personal data enable identity fraud and account takeover.
- The company’ll notify me if my data was stolen. Not always. Notification rules vary by region and may be delayed. Proactive scanning is safer.
- Public data isn’t dangerous. Publicly available pieces combined with breached data can fully recreate identity profiles.
Privacy hygiene: habits that matter long-term
Adopt these daily and weekly habits to lower long-term risk.
- Use unique passwords and a password manager.
- Enable MFA on all accounts, especially email and financial services.
- Periodically run an Email Dark Web Scan and look for stale services where your details may linger.
- Limit data you share publicly on social media; attackers build profiles from crumbs.
How regulators and insurance affect post-breach response
Legal obligations and cyber insurance terms now shape the recovery timeline and costs. Organizations must map notification timelines, breach reporting thresholds, and insurance claim procedures into incident playbooks. Individuals may also find remediation services presented by their banks or merchants; evaluate these offers carefully for completeness.
When to engage professionals (and what to expect)
Not every incident requires external help, but consider professional assistance if:
- You’re a business handling sensitive or regulated data.
- You detect lateral movement or persistent unauthorized access.
- You see evidence of your data being sold or broadly distributed.
Services typically provided: forensic investigation, containment, regulatory reporting support, identity restoration, and continuous Breaches Monitoring.
The economics of breaches: why prevention often pays
Breaches carry direct costs (remediation, fines) and indirect costs (reputation damage, lost customers). Investment in controls like Data Leak Prevention and ongoing Dark Web Monitoring tends to be far cheaper than the combined cost of breach fallout. Think of prevention as insurance that reduces both the probability and the impact of incidents.
Real world scenario: how an attacker moves from breach to fraud
- Attacker obtains an email and password from a breach.
- They validate the credential set across primary services (credential stuffing).
- Compromised accounts are used for financial theft, phishing, or lateral access into business networks.
- Aggregated PII is sold on the underground market.
- This chain underscores why Credentials Leak Detection and password uniqueness are so critical.
Practical technologies you should evaluate
The security market is crowded; focus on capability and integration:
- Dark Web Monitoring and Deep Web Scanning for early signals.
- Credentials Leak Detection automatically flags reuse and forces resets.
- Data Leak Prevention to prevent exfiltration from internal systems.
- Real-time threat Intelligence to contextualize alerts and prioritize response.
Integration with your SIEM, Essence platform, and incident response workflow is essential for efficiency and effectiveness.
Tips for communicating after a breach (for organizations)
Transparency builds trust. Follow these communication principles:
- Be timely and factual explain what happened succinctly.
- Offer concrete remediation steps for affected users (password resets, free dark web scan offers).
- Provide ongoing updates as investigations progress.
Avoid speculation; work with legal and PR to craft messages that protect users and the organization.
The human factor: training that actually works
Technical controls fail when humans make unsafe choices. Practical training focuses on:
- Realistic, scenario-based phishing simulations.
- Clear guidance on reporting suspicious messages.
- Role-based training for privileged users and support teams.
Combining behavior change with automation (such as blocking known malicious senders) dramatically reduces risk.
How to choose a reputable scanner or monitoring service
When selecting tools or providers, evaluate these factors:
- Coverage: Do they scan both indexed and deep- and dark-web sources? (Look for Deep Web Scanning and Dark Web Monitoring capabilities.)
- False positives: Quality analytic models reduce noise and improve response confidence.
- Actionability: Does the service include remediation guidance or only raw alerts?
- Privacy: Ensure the vendor handles your queries securely and won’t add your data to monitored lists.
Ask for sample Darkweb report outputs before committing so you can judge the usefulness.
3 4 Quick, high-impact actions (bullet list)
- Rotate passwords and enable MFA on your primary email now.
- Run an Email Dark Web Scan and a free dark web scan to see immediate exposure.
- Freeze credit or place fraud alerts if financial or identity data is present.
- For organizations: activate the incident response playbook and trigger Cyber Threat Analysis.
Long tail risks: identity theft, resale, and future exploitation
Even after immediate remediation, breached data can be used months or years later for identity theft, targeted scams, or account takeovers. That’s why continuous monitoring from Breaches Monitoring to periodic Check email data breach checks matters beyond the first 90 days.
Building resilience: a roadmap for 12 months

- Months 0–1: Contain, notify, reset credentials, offer immediate scans.
- Months 1–3: Conduct complete forensic and regulatory assessments; remediate root causes.
- Months 3–6: Deploy Data Leak Prevention and strengthen identity controls.
- Months 6–12: Mature detection with Real Time Threat Intelligence and rolling exercises.
This phased approach balances urgent action with strategic improvements.
Closing: your next 48 hours a prioritized action plan
In the next two days, focus on what reduces immediate exploitation risk:
- Reset passwords on high-value accounts and enable MFA.
- Run targeted Email data breach and free dark web scans for your primary addresses.
- Review financial statements and set transaction alerts.
- For organizations, isolate affected systems and notify regulators if required.
Responding fast and smart dramatically reduces the long-term consequences of the Latest Data Breach and strengthens your overall Reputation Management strategy.
Final note
A breach changes the threat landscape, but it doesn’t have to mean permanent harm. By combining rapid personal action, continuous monitoring (including Dark Web Monitoring and Deep Web Scanning), and organizational improvements like Data Leak Prevention and Credentials Leak Detection, you can limit damage, recover faster, and make future attacks much harder. Start with the prioritized 48-hour plan above absolute safety begins with immediate, measurable steps.
FAQs
How can I quickly check if my email was exposed?
Use an Email data breach scan or a reputable breach-check service to search known leak databases. These tools return matches and recommended next steps. Act immediately on any positive result.
Is a free dark web helpful scan?
A free dark web scan gives a quick signal of exposure, but may not cover deep sources comprehensively. Use it as an initial check, then follow up with more thorough monitoring if you see anything. Free scans are a good first line of defense.
What is the difference between Dark Web Monitoring and Deep Web Scanning?
Dark Web Monitoring focuses on marketplaces and forums where stolen data is traded. Deep Web Scanning reaches non-indexed or restricted areas that typical search engines miss. Together, they provide broader visibility.
Should I pay for identity restoration services after a breach?
Paid identity restoration can be valuable if sensitive identifiers were exposed or fraud occurred. Evaluate services for coverage, duration, and what remediation they actually perform. Your bank or insurer may also offer options.
How often should organizations run Breach Monitoring?
Continuous Breaches Monitoring is best; it provides real-time alerts and shortens detection time. At a minimum, conduct automated scans daily and supplement with periodic manual review. Rapid Detection reduces overall breach impact.